As we approach 2025, the field of cell culture is poised for transformative advancements that promise to enhance research and applications across biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and regenerative medicine. Experts in the industry, such as Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned cell culture specialist at BioInnovate Labs, have emphasized the critical importance of innovation in this area, stating, "The future of cell culture lies in our ability to leverage emerging technologies to improve efficiency and precision in cell handling." This sentiment reflects the collective anticipation and excitement surrounding the next wave of developments.

In recent years, we have witnessed significant shifts in techniques and methodologies that drive cell culture forward, from three-dimensional cultures to organ-on-a-chip technologies. As we unveil the top trends for 2025, we will explore how these advancements not only optimize traditional practices but also foster entirely new possibilities for personalized medicine and high-throughput screening. As stakeholders in the cell culture industry prepare for the future, understanding these innovations will be crucial for staying competitive and ensuring successful research and development processes. The evolution of cell culture techniques will undoubtedly shape the next generation of scientific exploration and discovery.
The field of cell culture is experiencing a significant transformation, particularly in bioreactor design, which is central to achieving enhanced culturing efficiency. Recent advancements have led to the development of innovative bioreactor systems, including single-use and perfusion bioreactors, which have shown a 30% increase in productivity over traditional systems. According to a market analysis by Grand View Research, the bioreactor market is projected to reach $3 billion by 2026, driven by these cutting-edge technologies. The use of advanced sensors and automated controls is allowing for real-time monitoring and adjustments, ultimately leading to optimized cell growth conditions.
In addition to productivity improvements, modern bioreactor designs cater to the growing demand for reproducibility and scalability in cell culture processes. For instance, the integration of microfluidics in bioreactor systems enables precise manipulation of culture conditions at a microscale, allowing researchers to maintain consistency across batches. A study from the Journal of Biotechnology highlighted that these advancements in bioreactor design not only streamline research but also significantly reduce the time required to bring biopharmaceutical products to market—reporting time savings of up to 40%. As the industry progresses, the continuous evolution of bioreactor technology will be vital to meeting the increasing demands for therapeutic protein production and cellular therapies.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into cell culture processes represents a significant advancement in biotechnology. By leveraging machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics, researchers can streamline the experimentation workflow, optimize cell growth conditions, and minimize variability in results. AI systems can analyze vast datasets generated from cell culture experiments, identifying patterns that are often imperceptible to the human eye. This capability not only enhances the reproducibility of experiments but also accelerates the development of new therapeutic strategies.
Moreover, AI-driven automation is revolutionizing the way cell cultures are managed. Robotics combined with AI can automate routine tasks such as feeding, monitoring cell health, and detecting contamination. This reduces human error and allows scientists to focus on more complex analytical tasks. By integrating AI into laboratory environments, researchers can achieve higher throughput and more efficient resource allocation, ultimately leading to a faster realization of breakthroughs in drug discovery and regenerative medicine. The synergy between AI and cell culture is poised to reshape the future of biological research and therapeutic development.
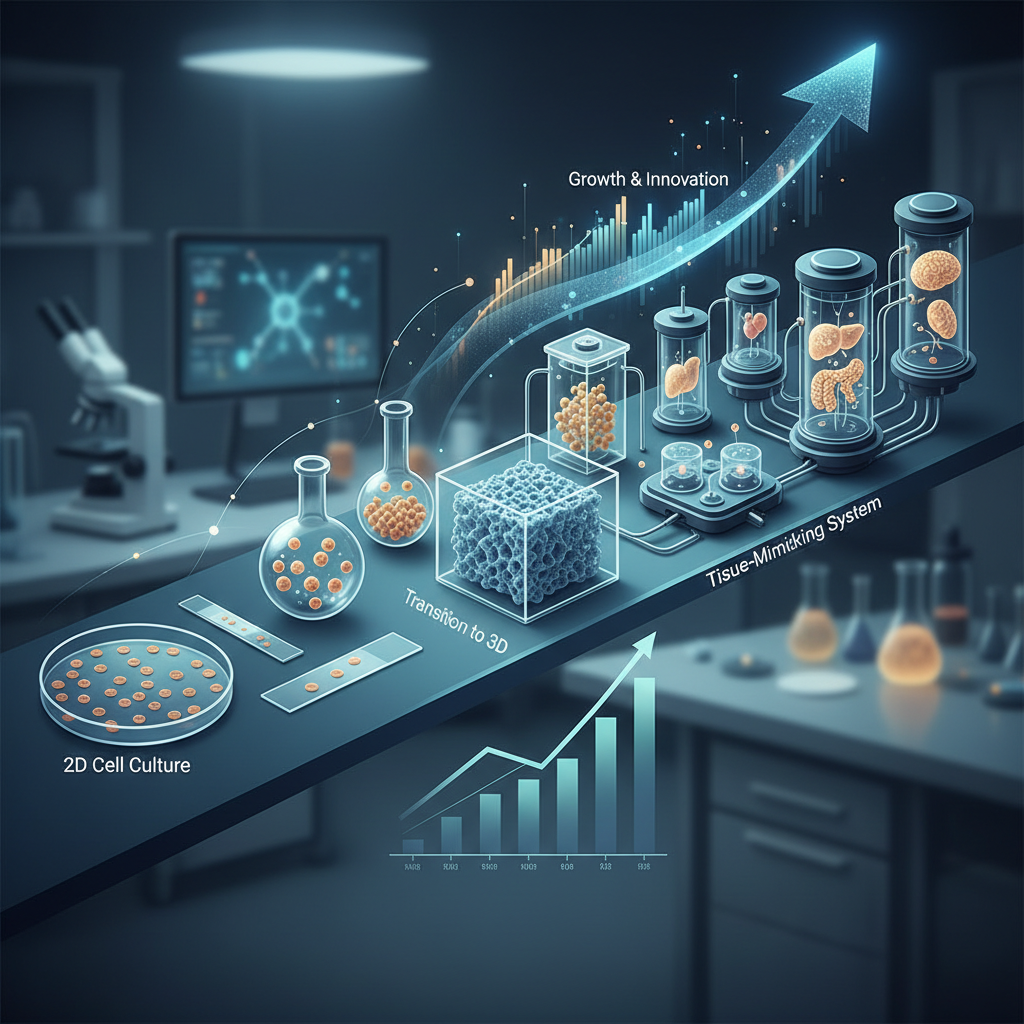
The evolution of 3D cell culture models is transforming the landscape of
biomedical research and regenerative medicine. As researchers seek more physiologically relevant environments,
3D models offer advantages over traditional 2D cultures by mimicking the tissue architecture and cellular
interactions found in vivo. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global 3D cell culture market is
projected to reach $2.4 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 24.8% from 2020. This
growth highlights the increasing adoption of 3D models in drug development, personalized medicine, and disease
modeling.
One of the emerging trends is the integration of bioprinting technologies in creating customizable
3D structures, leading to greater control over cell placement and
microenvironment conditions. Additionally, advancements in biomaterials are enabling the design of scaffolds
that closely replicate native tissue properties, further enhancing cell viability and functionality. As this
field progresses, researchers and companies alike will need to stay informed on best practices for optimizing
culture conditions and leveraging new materials.
Tip: When selecting a 3D cell culture model, consider the specific
application and required physiological relevance to ensure optimal results. Tip:
Collaborate with bioprinting specialists to leverage the latest technologies for creating bespoke tissue models
tailored to your research needs.

Recent innovations in cell line development and optimization are transforming the biotechnology landscape. Advances in insect cell-expression systems are enhancing the performance of cell lines, leading to increased yields and purities in therapeutic production.
Techniques such as iterative experimental design employing Bayesian optimization are being utilized to streamline the development of culture media, facilitating a more efficient optimization process for complex biological systems.
Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence into cell culture practices is revolutionizing workflows. Tools that automate processes not only reduce human error but also accelerate drug discovery timelines. As organizations aim to overcome challenges related to biosimilar scaling—encompassing process consistency, analytical excellence, and regulatory compliance—the role of advanced analytics becomes critical. This evolution in cell line development methodologies is crucial for improving the overall efficiency and reliability of biopharmaceutical production.
The impact of single-cell sequencing on cell culture methodologies is profound, revolutionizing our understanding of cellular diversity and behavior. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the single-cell sequencing market is projected to reach $7.8 billion by 2025, reflecting its increasing significance in research and clinical applications. This technique enables scientists to analyze the genetic material of individual cells, providing insights that traditional bulk sequencing methods cannot offer. As a result, researchers can identify rare cell populations and study their unique responses to treatments, greatly enhancing drug discovery and personalized medicine.
Tip: When considering single-cell sequencing technologies, ensure you evaluate platforms offering high throughput and sensitivity, as these are crucial for obtaining reliable data from minimal cell quantities.
Additionally, the integration of single-cell sequencing data with advanced cell culture techniques fosters a more detailed characterization of cellular behaviors. This synergy allows for the development of robust models that mimic in vivo conditions more accurately. A study published in Nature Biotechnology highlights that combining single-cell sequencing with organoid cultures may produce innovative models for studying complex diseases, paving the way for tailored therapeutic approaches.
Tip: Leverage computational tools that facilitate the analysis of single-cell data; these resources can significantly streamline your research process and provide deeper insights into cellular mechanisms.
| Trend | Impact on Cell Culture | Key Techniques | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Cell Sequencing | Enables detailed analysis of cell heterogeneity | RNA-Seq, DNA-Seq | Better understanding of cell dynamics and differentiation |
| 3D Cell Culture Techniques | More physiologically relevant environments | Bioprinting, Organoids | Improved drug response models |
| Microfluidics | Enhances experimental control and reduces sample usage | Droplet-based systems, Lab-on-a-chip | Higher throughput screening |
| Artificial Intelligence in Cell Analysis | Facilitates data interpretation and predictive modeling | Machine Learning Algorithms, Data Mining | Faster insights into cellular behavior |
| CRISPR and Gene Editing | Allows precise modification of cell genomes | Gene Knockout, Gene Insertions | Creation of customized cell lines for research |