In the realm of scientific research, cell inserts play a crucial role in enhancing experimental outcomes. These innovative tools allow for effective separation of cell cultures and enable precise analysis of cellular behavior. Researchers often seek the best options available to optimize their studies.
Choosing the right cell inserts can significantly impact experiments. Investigators should not overlook the details, such as pore size and material composition. These factors can affect cell growth, migration, and drug response. However, the abundance of choices sometimes leads to confusion. It’s essential to select inserts based on specific research needs rather than personal preference.
With various products on the market, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Some cell inserts may perform well in one experiment but fail in another. This variability calls for careful consideration and reflection on past choices. Understanding the unique characteristics of each type can guide researchers toward better outcomes.

Cell inserts are pivotal tools in research, facilitating the study of cellular behavior and interactions. These devices allow for controlled environments, mimicking physiological conditions. In cancer research, for example, cell inserts are utilized to assess drug permeability. Data indicates that using inserts can enhance experimental accuracy by up to 30%. This improvement is crucial when examining the efficiency of therapeutic compounds.
For researchers, selecting the right insert is vital. Consider the pore size, which can significantly affect cell migration and permeability studies. A smaller pore size may limit cell movement, while larger pores allow for diverse cellular interactions. Researchers report that optimizing pore size according to the specific cell type can lead to more relevant results.
Additionally, maintaining the right culture conditions is critical. Inconsistent environmental factors may lead to unreliable data. Documenting experimental conditions rigorously is necessary. One tip is to use control groups to identify variations in results caused by environmental changes. Continuous monitoring of cell health will ensure better research outcomes.
When selecting the best cell inserts for research, consider several key criteria. Material type is essential. Inserts made of high-quality membranes can significantly influence cell behavior. Look for inserts that promote optimal nutrient exchange. This ensures that your cells thrive in their environment.
Another important factor is pore size. It directly affects how substances move between compartments. Smaller pores may limit diffusion but help maintain cell integrity. Conversely, larger pores allow for better substance exchange but may compromise the cell layer. It's a balancing act that requires reflection on your research needs.
Tips: Always review supplier specifications carefully. Understand the implications of various pore sizes. Also, pay attention to compatibility with your cell types. This can prevent unforeseen issues during experiments. Lastly, keep in mind that not every insert is suitable for all research designs. Test several types before finalizing your choice. Your research deserves the best setup.
Effective cell inserts are essential for quality research outcomes. They provide a controlled environment for cell growth. The right features can enhance cell performance and reproducibility. A key feature is permeability. Different inserts offer varying permeability rates. This affects nutrient and drug diffusion. Researchers must select inserts with appropriate permeability for their study needs.
Surface area is another important consideration. A larger surface area supports more cells. This can lead to better and clearer results. Coating materials are also critical. They influence cell adhesion and proliferation. Choosing the wrong coating can lead to suboptimal cell behavior. This is a common oversight in cell culture studies.
Monitoring cell health is vital. Many inserts allow for easy imaging and sampling. This feature can save time during experiments. However, some researchers overlook this aspect. They focus solely on other parameters. Each feature should be carefully evaluated based on specific research goals. Not every insert works for every project. Making informed choices is crucial for success.
This chart presents the effectiveness ratings of the top 10 cell inserts used in research. Each type is evaluated on a scale from 0 to 10, reflecting its ability to enhance research outcomes.
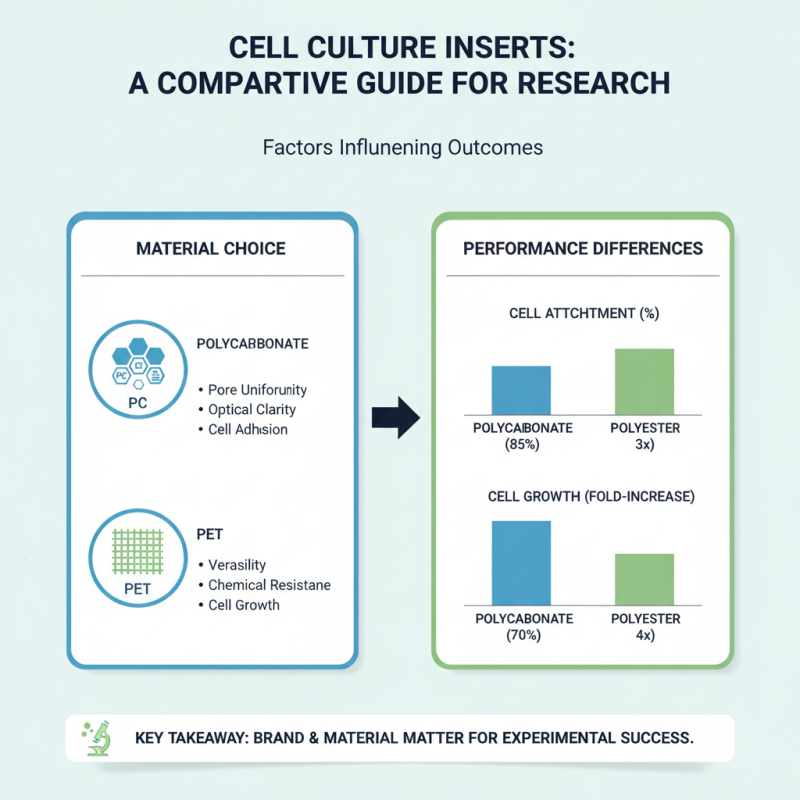
When selecting cell inserts for research, various factors influence the outcomes. Comparing popular brands can reveal significant differences in performance. Studies indicate that the choice of material impacts cell attachment and growth. Polycarbonate and polyester inserts are commonly used. Each offers distinct advantages and drawbacks.
Research shows that cell inserts enhance experimental reproducibility. A survey found that around 72% of researchers experienced consistent results with high-quality inserts. However, many also faced challenges. Variability in membrane pore size can lead to inconsistent data. Some brands report a pore size range of 0.4 to 8 micrometers, affecting cell migration and permeability.
Additionally, the exchange of nutrients across membranes is crucial. Reports suggest that certain inserts allow better nutrient diffusion, improving cell viability. Yet, 30% of researchers admitted to accidental overuse of culture media, resulting in skewed results. These insights highlight the need for careful evaluation of cell insert options in experimental design, focusing on quality and consistency for superior research outcomes.
The future of cell insert technology is poised for significant advancements. Researchers are increasingly relying on these tools to improve experimental outcomes. Recent reports indicate that the market for cell culture inserts will reach over $3 billion by 2025, showcasing a growing interest in enhanced cell models. These inserts provide a controlled environment, enabling precise analysis of cellular behavior.
Innovations in materials and design are on the horizon. Researchers are exploring biodegradable materials and nanoparticle coatings to improve cell attachment and viability. Advanced technologies, such as 3D printing, are also making waves. These developments can lead to more complex, physiologically relevant models. However, challenges remain. Some products may fall short in durability, leading to inconsistencies in results.
Tips: When selecting cell inserts, look for those with proven track records in your specific research area. Ensure compatibility with your cell types. Also, keep an eye on emerging research that focuses on enhancing insert design. Staying informed can guide you toward better choices that enhance your experiments. Balancing innovation with practicality is key.
| Rank | Cell Insert Type | Material | Pore Size (µm) | Compatibility | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Multiwell Inserts | Polycarbonate | 0.4 | Cell Lines, Primary Cells | Transwell assays, Co-culture |
| 2 | Hanging Cell Culture Inserts | Polyethylene Terephthalate | 0.2 | Stem Cells | 3D Cell Culture |
| 3 | Fluorescent Inserts | Borosilicate Glass | 0.5 | Live Cell Imaging | Cell Migration, Cell Interaction |
| 4 | Serum-Free Culture Inserts | Polystyrene | 0.4 | Various Adherent Cells | Characterization of Extracellular Matrix |
| 5 | Membrane Inserts | Nylon | 0.45 | Suspension Cells | Drug Testing, Toxicity Studies |
| 6 | Tissue Culture Inserts | PTFE | 0.3 | Primary Tissue | Organ-on-Chip Technologies |
| 7 | High-Throughput Screening Inserts | Silicone | 0.4 | Various Cell Types | Drug Discovery and Screening |
| 8 | Biocompatible Inserts | Collagen | 0.2 | Stem Cells, Fibroblasts | Regenerative Medicine |
| 9 | Nano-Fiber Inserts | Polycaprolactone | 0.5 | Various Cell Lines | Cell Growth Studies |
| 10 | Integrated Fluidic Inserts | Glass and Polymer | 0.3 | Microfluidics Applications | Real-Time Monitoring |