The biology of a human is a fascinating and complex subject that underpins every aspect of our existence. From the intricate design of our cellular structures to the sophisticated systems that regulate our bodily functions, human biology is an essential field of study that reveals how our physical and biochemical makeup shapes our lives. Understanding the biology of a human allows us to appreciate the remarkable capabilities of our bodies, the processes that support life, and the ways in which our biology influences our behavior, health, and interactions with the environment.
In exploring the biology of a human, we delve into various dimensions, including genetics, physiology, and anatomy. These disciplines not only provide insight into how we function as individuals but also highlight the links between biology and factors such as disease susceptibility, behavioral traits, and even social structures. By examining the nuances of human biology, we can better grasp the implications of our biological makeup on a personal and societal level, paving the way for advancements in medicine, public health, and overall well-being. Understanding our biology is not merely an academic pursuit; it has profound implications for enhancing the quality of our lives and addressing the challenges that confront humanity today.

Human biology is a vast discipline that encompasses the study of the body’s structure, function, and systems. At its core, it examines the cellular and molecular foundations of human life. Understanding the anatomy—how organs and systems are organized—and physiology—the functioning of those organs and systems—provides essential insight into how we operate as living beings. This knowledge is foundational not just for the medical field but also for understanding health, development, and aging processes.
Key concepts in human biology include genetics, metabolism, and homeostasis. Genetics explains how traits are inherited and how they can influence our health and predisposition to diseases. Metabolism encompasses the biochemical processes that provide energy for cellular activities, crucial for growth and maintenance. Homeostasis refers to the body’s ability to maintain stable internal conditions despite external changes, ensuring that organs function optimally. These concepts interconnect numerous aspects of health and disease, influencing lifestyle choices and medical interventions, thereby shaping the way we lead our lives and manage our well-being.
Human cells are the fundamental building blocks of life, performing essential functions that sustain bodily processes. Each human cell averages around 10-30 micrometers in diameter, primarily consisting of a nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane. According to the National Institutes of Health, the human body is composed of approximately 37.2 trillion cells, which vary significantly in form and function—ranging from muscle cells and neurons to epithelial cells. This diversity allows for specialized tasks that contribute to overall homeostasis and health, demonstrating the intricate relationship between cellular structure and function.
Understanding cellular biology can greatly enhance our approach to health and wellness. For example, research indicates that maintaining healthy mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell, is vital for energy production and has been linked to longevity and fitness. A study published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry highlighted that optimizing mitochondrial function could improve physical performance and reduce the risk of age-related diseases.
**Tips:** Consider incorporating a diet rich in antioxidants such as berries, nuts, and green leafy vegetables to aid cellular health. Additionally, regular physical activity not only promotes cellular health but also stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis, leading to enhanced energy levels and vitality. Prioritizing sleep is crucial as well, as restorative sleep enables optimal cellular repair processes essential for longevity.
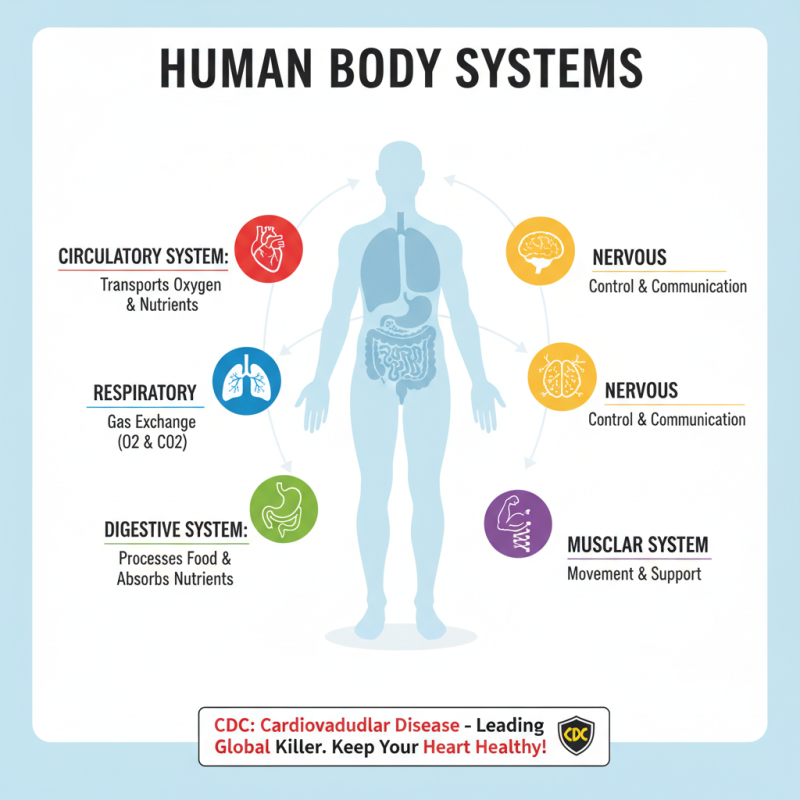
The human body operates through a complex interplay of organ systems, each contributing to the overall functionality required for sustaining life. The primary systems include the circulatory, respiratory, digestive, nervous, and muscular systems, which work collaboratively to maintain homeostasis and ensure the survival of the organism. For instance, the circulatory system is responsible for transporting oxygen and nutrients to cells, while simultaneously removing carbon dioxide and waste products. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), cardiovascular disease remains a leading cause of death globally, emphasizing the importance of a well-functioning circulatory system for overall health.
Moreover, the integration of the nervous and endocrine systems is crucial for regulating bodily functions. These systems communicate through complex biochemical signals and neural pathways, enabling responses to internal and external stimuli. A report from the World Health Organization highlights that chronic stress can disrupt these systems, leading to various health issues such as anxiety and obesity. Understanding how these organ systems interact not only illuminates the intricacies of human biology but also underscores the significance of maintaining their health for preventing diseases and promoting longevity. Together, these systems exemplify the remarkable design of the human body, showcasing how interconnectivity leads to resilience and adaptability in our daily lives.
Genetics and heredity serve as the foundational blueprint for human development, influencing everything from physical attributes to susceptibility to diseases. Human DNA, composed of genes inherited from both parents, outlines the instructions for building and maintaining the body.
These genes dictate traits such as eye color, height, and even complex behaviors. Importantly, variations in these genes can result in differences in health outcomes, highlighting the intricate relationship between genetics and individual well-being.
The impact of genetics extends into various aspects of life, including health care and disease prevention. Understanding one's genetic makeup can inform decisions related to lifestyle choices and medical interventions. For instance, individuals with a family history of specific conditions may opt for genetic testing to assess their risk and take proactive measures.
Moreover, advancements in genetic research are yielding insights into how certain genes can influence the efficacy of treatments, paving the way for personalized medicine. By recognizing the role of genetics and heredity, we can better appreciate the complexity of human biology and its implications for health across generations.

Human biology profoundly influences our health, disease prevalence, and overall well-being. At the cellular level, the human body consists of approximately 37.2 trillion cells, each performing essential functions that maintain homeostasis. These cells are influenced by genetic factors, which dictate everything from metabolic rates to susceptibility to various diseases. For instance, a report from the World Health Organization indicates that genetic predisposition accounts for about 30% of an individual's risk for developing type 2 diabetes, underscoring the complex interplay between our biology and health outcomes.
Moreover, human biology affects the way we respond to environmental factors and lifestyle choices. The National Institute of Health has highlighted that nearly 60% of chronic diseases, such as heart disease and obesity, are linked not only to genetic codes but also to lifestyle factors associated with daily living. Factors like diet, exercise, and stress management play crucial roles in determining the expression of our genes and, consequently, our health. As we understand the biological mechanisms behind these interactions, it becomes evident that interventions aimed at improving health must take into account both biological predispositions and environmental influences. This holistic perspective can lead to more effective prevention strategies and improved health outcomes for populations at large.