Cell culture techniques have advanced significantly in recent years, with innovative methods enhancing the way researchers study cellular behavior and interactions. One such advancement is the use of cell inserts, which have emerged as essential tools in the field of tissue engineering and cellular research. These specialized devices allow for the creation of a controlled microenvironment, fostering the growth and differentiation of cells while facilitating the investigation of various physiological and pathological processes.
The incorporation of cell inserts in culture systems enables scientists to simulate in vivo-like conditions, thereby improving the relevance of their experimental findings. Through the use of cell inserts, researchers can easily study cell migration, permeability, and interaction between different cell types. These applications are crucial for understanding complex biological systems and developing therapeutic strategies for diseases. As research continues to evolve, the importance of optimizing cell culture methods through tools like cell inserts cannot be overstated, paving the way for breakthroughs in biomedicine and regenerative medicine.

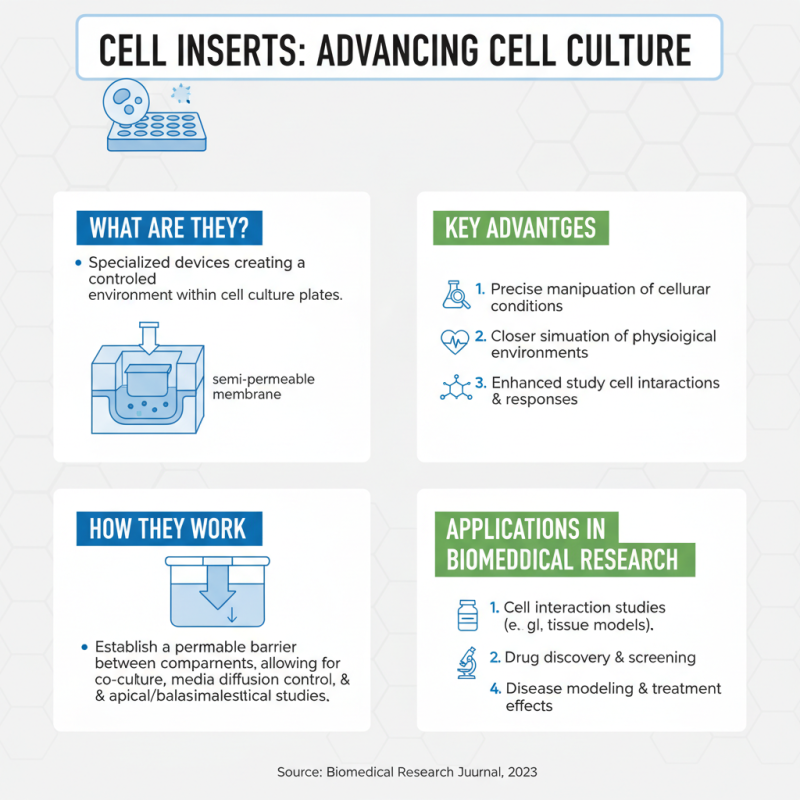
Cell inserts have emerged as pivotal tools in enhancing cell culture techniques, providing significant advantages for various applications in biomedical research. These specialized devices create a controlled environment for cells, allowing for more precise manipulation of cellular conditions. By establishing a barrier between different compartments, cell inserts enable researchers to simulate physiological conditions more closely, which is particularly beneficial for studying cell interactions, drug responses, and the effects of various treatments on cellular behavior.
The use of cell inserts facilitates advanced techniques such as co-culture systems, where two distinct cell types can be grown simultaneously. This is advantageous in modeling tissue environments and understanding complex cellular interactions. Additionally, cell inserts enable the testing of permeability and transport mechanisms across membranes, providing insights into drug delivery systems and absorption in tissues. Furthermore, modifications to the material and surface properties of these inserts can enhance cell attachment and differentiation, thus broadening their application in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
Cell inserts have revolutionized the field of cell culture, offering researchers the ability to create controlled microenvironments for various cellular applications. These inserts come in different types, each tailored for specific experimental needs. For instance, transwell inserts are widely used to study cell migration and invasion, allowing for the analysis of cellular responses to chemotactic factors. On the other hand, membrane inserts facilitate the examination of epithelial barrier function, providing insights into permeability and drug absorption.
When choosing a cell insert, it’s crucial to consider the pore size and membrane material, as these factors directly affect cell behavior and function. For co-culture systems, using inserts that allow for direct cell-to-cell communication is essential for accurate data interpretation. Additionally, researchers should account for the compatibility of the insert with their specific cell lines to ensure optimal growth conditions and experimental outcomes.
Tips: Always perform a pilot experiment to determine the best conditions for your specific application. Checking the integrity of the membrane before and after the experiment can help gauge its suitability for your study. Moreover, consider the use of specialized media that complements the insert's design, as this can significantly impact cell viability and the reproducibility of your results.
| Type of Cell Insert | Material | Porosity | Common Applications | Cell Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transwell Inserts | Polycarbonate | 0.4 μm | Cell migration, invasion assays | Cancer cells, epithelial cells |
| Membrane Inserts | PET | 0.2 μm | Barrier function studies | Endothelial cells, fibroblasts |
| Co-culture Inserts | Collagen | Varies | Studying cell-to-cell interactions | Immune cells, tumor cells |
| 3D Cell Culture Inserts | Matrigel | Varies | Tissue engineering, drug testing | Stem cells, organoids |
Cell inserts have emerged as a critical tool for enhancing in vitro studies in cell culture techniques, providing a versatile platform for a variety of applications. One of the primary benefits of using cell inserts is their ability to create a controlled microenvironment. This feature allows researchers to distinguish between apical and basolateral sides of cultured cells, facilitating studies on cellular absorption, secretion, and interaction. According to a report from Research and Markets, the global market for cell culture technology is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.8% from 2021 to 2026, underscoring the increasing reliance on advanced cell culture methods like those utilizing cell inserts.
Moreover, cell inserts can significantly improve the relevance of in vitro models by mimicking physiological conditions more accurately. For instance, studies have demonstrated that using inserts can enhance the functionality of epithelial cells, promoting the development of tighter junctions, which is essential for barrier function in drug absorption studies. A systematic review in the journal “Tissue Engineering” highlighted that models incorporating cell inserts exhibited more accurate predictive capabilities for drug permeability compared to traditional flat cultures, further supporting their importance in pharmacokinetics research. These advancements in cell insert technology not only enhance experimental outcomes but also contribute to more efficient drug development processes.
When implementing cell inserts in laboratory protocols, adhering to best practices is essential for achieving optimal results. First, researchers should ensure that they select the appropriate type of insert based on the cell type and specific application. Different inserts have varying pore sizes and materials, which can significantly affect cell behavior and interactions. It's advisable to familiarize yourself with the characteristics of the insert, such as permeability and adhesion properties, to select the most suitable one for your experiments.
Once the appropriate cell insert is chosen, proper handling and sterilization techniques should be employed to prevent contamination. This involves using aseptic techniques and ensuring that all materials are sterile before use. Moreover, accurately seeding cells into the inserts is crucial; maintaining consistent cell numbers across experiments will lead to more reliable data. Researchers should also consider the environmental conditions within the insert system, such as the medium volume and incubation parameters, as these can influence cell growth and functionality. Establishing a routine for monitoring cell health and performing periodic changes of the media can help maintain optimal culture conditions throughout the experiment.
Lastly, documentation of all procedures and results is vital for reproducibility and validation of findings. Keeping detailed records of insert usage, cell lines used, and any variations in protocols assists in drawing accurate conclusions and facilitates future experiments. By prioritizing these best practices, researchers can effectively leverage cell inserts to enhance their cell culture techniques and applications.
Recent advancements in cell culture insert technology are paving the way for future trends that promise to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of cellular research. Innovations in materials and design, including the use of biodegradable membranes and customizable inserts, are making it easier for researchers to tailor their experiments to specific needs. These improvements not only facilitate optimal nutrient and gas exchange but also reduce the risk of contamination and improve reproducibility across experiments. As the understanding of cellular behavior evolves, the integration of smart technology into cell culture inserts, such as sensors that monitor environmental conditions in real time, is becoming increasingly feasible.
Moreover, the rise of 3D cell culture models is shaping the future landscape of cell culture inserts. Researchers are now exploring how these advanced models can mimic in vivo environments more closely, providing more relevant results. Inserts that can support both 2D and 3D cultures will likely become more mainstream, enabling a seamless transition between different experimental setups. As cell culture techniques continue to evolve, the focus on biocompatibility and ethical considerations will drive the development of inserts that not only improve research outcomes but also comply with the growing demand for sustainability in scientific practices.