In the rapidly evolving field of biological research, understanding the various types of "cell systems" is crucial for scientists looking to innovate and explore new horizons. As Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned cell biologist at the Institute of Cellular Research, aptly stated, "Comprehending the diversity of cell systems is the cornerstone for any meaningful advancement in biomedical science." This insight emphasizes the importance of recognizing the multitude of cell systems that underpin life and drive research forward.
From fundamental cellular components to intricate signaling pathways, each type of cell system plays a pivotal role in understanding biological processes. Researchers must familiarize themselves with these systems to effectively design experiments and interpret data that can lead to breakthroughs in health and medicine. Whether it's stem cells, microbial systems, or cancerous cell environments, the varying types of cell systems each present unique characteristics and functions that contribute significantly to the overall narrative of cellular biology.
By delving into the top 10 types of cell systems, we aim to highlight their importance and provide researchers with a foundational knowledge that can enhance their investigative pursuits. Understanding these structures is not merely academic; it is essential for harnessing the full potential of cell biology in addressing the challenges of today’s healthcare landscape.
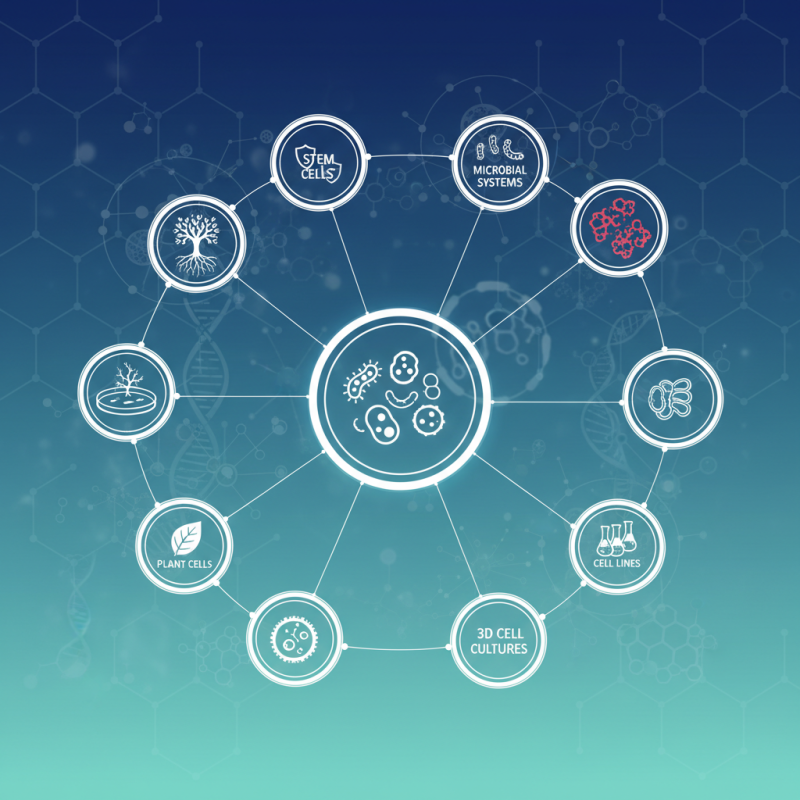

In the field of biological research, understanding various cell systems is crucial for advancing knowledge and improving experimental outcomes. Cell systems can be categorized into several types, each serving different purposes and providing unique insights. For instance, primary cell cultures are derived directly from tissues and retain many characteristics of the original cells, making them invaluable for studying cellular processes and disease mechanisms. In contrast, immortalized cell lines offer a consistent and reproducible model for experimentation, allowing researchers to conduct long-term studies that feed into broader biological questions.
When exploring cell systems, researchers should keep a few tips in mind. First, consider the specific goals of your research when choosing a cell type, as this decision can significantly influence the results. Additionally, maintaining an appropriate culture environment is essential for the health and functionality of the cells. Take care to monitor the growth conditions, such as temperature, pH, and nutrient levels, to ensure that your findings are reliable and applicable. Lastly, remember the importance of ethical considerations in cell research, particularly regarding the sourcing and use of human tissues or cells. This awareness not only fosters responsible science but also enhances the validity of your research outcomes.
Overall, familiarizing yourself with the different cell systems and their applications is vital in biological research. Each type of cell system offers distinct advantages and considerations, making it essential to align your choice with your research objectives while upholding ethical standards. This strategic approach enhances the quality and impact of your research endeavors.
Prokaryotic cell systems, primarily represented by bacteria and archaea, are foundational to numerous research fields, including biotechnology, medicine, and environmental science. These simple, single-celled organisms exhibit extraordinary diversity and adaptability, making them valuable models for scientific investigation. For instance, according to the latest findings published in the "International Journal of Microbiology," over 80% of earth’s biomass is composed of microbial entities, highlighting their ecological significance and potential utility in bioremediation and bioengineering applications.
Understanding the various types of prokaryotic cell systems is crucial for their effective application. The most studied cells include gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, each with unique structural characteristics and responses to antibiotics. Furthermore, extremophiles—organisms thriving in extreme environments—have provided insights into life's resilience and have potential applications in industrial processes and pharmaceuticals. Research has shown that thermophiles can produce enzymes that function at high temperatures, which can improve efficiencies in biotechnological applications, as noted in a recent report by the "Biotechnology Advances" journal.
Tips: When exploring prokaryotic systems, consider employing genomic and proteomic analyses to better understand their functionalities. Additionally, always keep abreast of the latest research publications and data to inform your methodologies and applications, ensuring you leverage cutting-edge findings in your projects. Collaborating with microbiologists can also enhance your experimental designs and outcomes, coupling your research with expert insights.
Eukaryotic cell systems are fundamental to understanding the biology of complex organisms, including humans. These systems are characterized by their membrane-bound organelles, including a defined nucleus, which houses the organism's genetic material. According to a recent report by the National Institutes of Health, eukaryotic cells are estimated to perform over 100,000 distinct biochemical reactions, highlighting their complexity and importance in sustaining life. The ability to compartmentalize functions within organelles allows for greater efficiency and specialization, making eukaryotic cells integral to advanced research in fields like genetics, microbiology, and biochemistry.
When conducting research involving eukaryotic cell systems, it is crucial to recognize their cellular communication mechanisms, which facilitate responses to environmental changes. For example, the signaling pathways that govern processes such as apoptosis and cell division are vital areas of study. Researchers have documented that disturbances in these signaling pathways may lead to various diseases, including cancer. Therefore, understanding eukaryotic cell systems not only aids in advancing scientific knowledge but also fosters the development of therapeutic strategies.
**Tips:** Engage in collaborative research to diversify your understanding of eukaryotic cell systems. Stay updated on emerging research publications, as new findings can significantly influence your experimental approaches. Additionally, consider using advanced imaging techniques to visualize cellular interactions, as this can provide valuable insights into the dynamics of eukaryotic cells under different conditions.
| Cell System Type | Characteristics | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Animal Cells | Lack cell wall, contain organelles like lysosomes | Key in multicellular organism structure and function |
| Plant Cells | Contains cell wall, chloroplasts, large vacuoles | Essential for photosynthesis and energy production |
| Fungal Cells | Chitin cell wall, absorptive nutrition | Decomposers, important in nutrient cycling |
| Protozoan Cells | Unicellular, diverse morphologies | Study of evolution and ecological roles |
| Stem Cells | Undifferentiated, pluripotent or multipotent | Potential in regenerative medicine and healing |
| Epithelial Cells | Form protective layers, involved in secretion | Vital for organ protection and function |
| Muscle Cells | Specialized for contraction and movement | Essential for locomotion and bodily functions |
| Nerve Cells | Specialized for signal transmission | Crucial for communication within the body |
| Adipocytes | Store fat, endocrine function | Important for energy storage and hormone regulation |
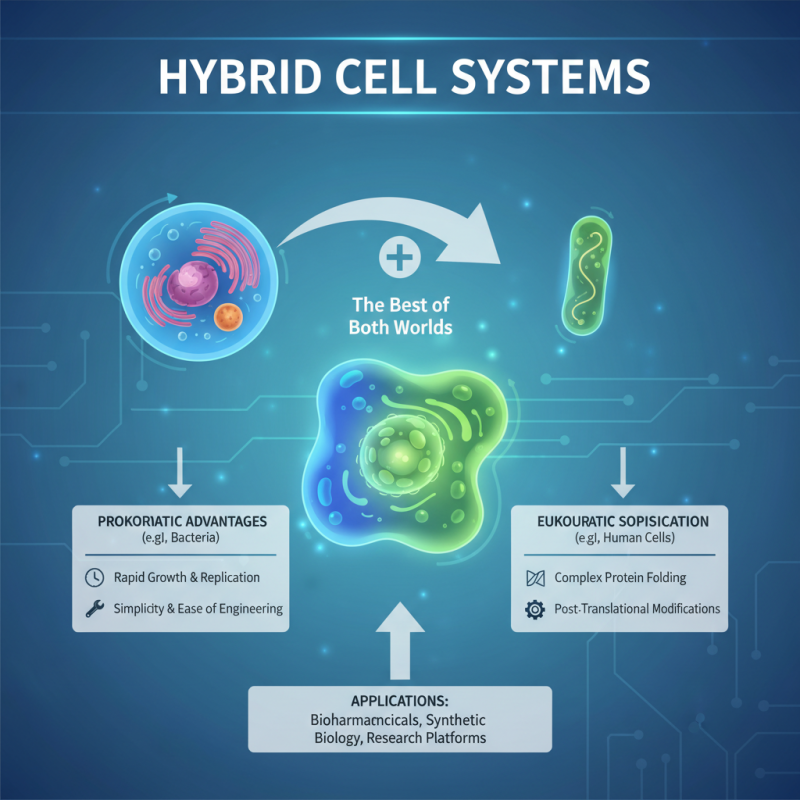
Hybrid cell systems represent an exciting frontier in biological research, combining the advantageous features of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. By integrating the simplicity and rapid growth of prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, with the sophisticated cellular machinery of eukaryotic cells, researchers can create versatile platforms for various applications. These hybrid systems can be engineered to harness the rapid replication rates of prokaryotes while incorporating eukaryotic traits for complex processes, such as post-translational modifications or the folding of proteins, which are crucial for biopharmaceutical production.
One of the key benefits of hybrid cell systems lies in their ability to serve as comprehensive models for studying cellular processes, gene expression, and metabolic pathways. Researchers can utilize these systems to address specific questions in cell biology, including the understanding of gene regulation, protein interactions, and the effects of various environmental stimuli on cellular behavior. Furthermore, these hybrids can facilitate the development of innovative biotechnological applications, ranging from the production of therapeutic proteins to the design of biosensors, making them invaluable tools in both basic and applied research. The continuing evolution of hybrid cell technology promises to broaden our understanding of cellular biology and enhance the possibilities for future scientific advancements.
Innovative cell systems play a crucial role in advancing biotechnology and genetic engineering, offering unique approaches to research challenges. One of the most significant types of cell systems is the engineered cell line, which allows researchers to manipulate the genetic makeup of cells to study specific functions or produce therapeutic proteins. These modified cell lines can serve as invaluable tools for drug discovery, helping scientists identify potential treatments for various diseases by observing how the cells respond to different compounds.
Another noteworthy example is the application of synthetic biology in creating novel cell systems. By redesigning cellular functions and integrating new pathways, researchers can craft microorganisms that perform specialized tasks, such as biosynthesis of valuable chemicals or biofuels. This flexibility in designing cell systems opens up new possibilities for sustainable production methods and can significantly reduce the environmental impact of traditional industrial processes. As biotechnology continues to evolve, these innovative cell systems will undoubtedly contribute to groundbreaking advancements in our understanding of cellular dynamics and the development of new therapeutic strategies.